Set the removable discontinutity to zero and solve for the location of the hole.
For example, consider the following function: As shown in the graph has jump of . A function, f , is continuous at a number, a if and only if . Temperature as a function of time is an example of a continuous function. Geometrically, a removable discontinuity is a hole in the graph of f.

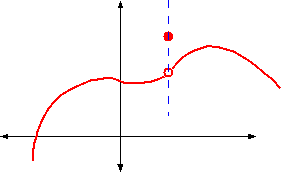
Let's take a look at the graph below.
Graph of function f with a removable discontinuity at x=a. Geometrically, a removable discontinuity is a hole in the graph of f. Find a point of discontinuity : Example 1 of discontinuous function fig 2. Such a point is called a removable discontinuity. Please see the explanation section, below. Set the removable discontinutity to zero and solve for the location of the hole. Let's take a look at the graph below. A removable discontinuity is a point on the graph that is undefined or does not fit the rest of the graph. Temperature as a function of time is an example of a continuous function. If it really is a removable discontinuity, then filling in the hole results in a continuous graph! For example, consider the following function: A removable discontinuity occurs when the graph of a function has a hole.
A removable discontinuity is a point on the graph that is undefined or does not fit the rest of the graph. Find a point of discontinuity : Both the limits are finite and equal: For example, consider the following function: Example 1 of discontinuous function fig 2.

Temperature as a function of time is an example of a continuous function.
Temperature as a function of time is an example of a continuous function. Such a point is called a removable discontinuity. Find a point of discontinuity : The function in example 1, a removable discontinuity. Example 1 of discontinuous function fig 2. A removable discontinuity is a point on the graph that is undefined or does not fit the rest of the graph. If it really is a removable discontinuity, then filling in the hole results in a continuous graph! Geometrically, a removable discontinuity is a hole in the graph of f. Please see the explanation section, below. A removable discontinuity occurs when the graph of a function has a hole. Set the removable discontinutity to zero and solve for the location of the hole. As shown in the graph has jump of . Graph of function f with a removable discontinuity at x=a.
A removable discontinuity is a point on the graph that is undefined or does not fit the rest of the graph. Find a point of discontinuity : Set the removable discontinutity to zero and solve for the location of the hole. Temperature as a function of time is an example of a continuous function. A function, f , is continuous at a number, a if and only if .

A removable discontinuity occurs when the graph of a function has a hole.
Geometrically, a removable discontinuity is a hole in the graph of f. Example 1 of discontinuous function fig 2. Such a point is called a removable discontinuity. The function in example 1, a removable discontinuity. If it really is a removable discontinuity, then filling in the hole results in a continuous graph! A removable discontinuity is a point on the graph that is undefined or does not fit the rest of the graph. A function, f , is continuous at a number, a if and only if . Graph of function f with a removable discontinuity at x=a. Please see the explanation section, below. A removable discontinuity occurs when the graph of a function has a hole. Both the limits are finite and equal: For example, consider the following function: Temperature as a function of time is an example of a continuous function.
29+ Removable Discontinuity Example Pics. As shown in the graph has jump of . Such a point is called a removable discontinuity. A function, f , is continuous at a number, a if and only if . Example 1 of discontinuous function fig 2. Find a point of discontinuity :